Dogs can suffer from various skin conditions that can cause discomfort or indicate underlying health issues. Here are some common skin conditions in dogs and their typical signs:
1. Allergies
- Types: Can be caused by food, environmental factors (like pollen or dust mites), or contact allergens (like certain fabrics).
- Signs: Itching, redness, swelling, hot spots, and possibly ear infections. You might also notice watery eyes or sneezing.
2. Flea Allergy Dermatitis
- Cause: Allergic reaction to flea saliva.
- Signs: Intense itching, redness, and hair loss, particularly around the tail base, lower back, and legs.
3. Hot Spots (Acute Moist Dermatitis)
- Cause: Often caused by itching or irritation that leads to self-trauma.
- Signs: Red, inflamed, and moist areas of skin, usually accompanied by itching or discomfort. The affected area can become infected if not treated.
4. Ringworm
- Cause: A fungal infection (not a worm).
- Signs: Circular patches of hair loss with red, scaly skin. Ringworm can be contagious to other pets and humans.
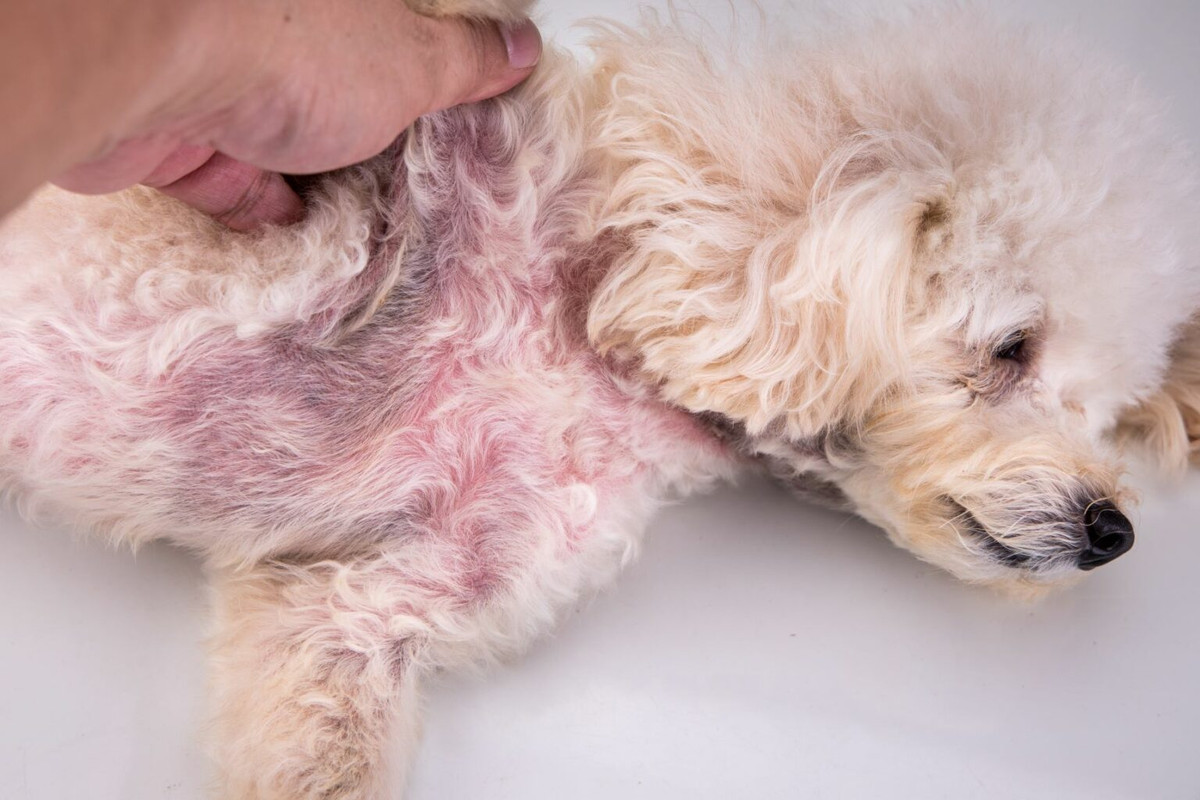
5. Mange
- Types: Sarcoptic mange (caused by Sarcoptes mites) and Demodectic mange (caused by Demodex mites).
- Signs: Sarcoptic mange causes intense itching, hair loss, and scabs. Demodectic mange often leads to localized or generalized hair loss and may cause secondary bacterial infections.
6. Pyoderma
- Cause: Bacterial infections of the skin.
- Signs: Redness, pustules, swelling, and sometimes an unpleasant odor. Pyoderma can occur due to underlying conditions like allergies or hormonal imbalances.
7. Seborrhea
- Types: Seborrheic dermatitis (oily) or dry seborrhea (flaky).
- Signs: Oily or dry, flaky skin, and a greasy or scaly appearance. It may also be associated with a strong odor and can cause itching.
8. Dermatitis
- Types: Contact dermatitis (due to contact with irritants) or atopic dermatitis (related to environmental allergies).
- Signs: Red, inflamed skin, itching, and possibly secondary infections. Contact dermatitis is often localized to the area of contact.
9. Hypothyroidism
- Cause: Underactive thyroid gland.
- Signs: Dry, flaky skin, hair loss, and potentially changes in coat quality. Dogs may also exhibit lethargy and weight gain.
10. Cushing’s Disease
- Cause: Overproduction of cortisol by the adrenal glands.
- Signs: Thin skin, hair loss, and potential for easy bruising. Dogs may also exhibit increased thirst, urination, and appetite.
11. Vitiligo
- Cause: Loss of pigmentation in the skin.
- Signs: Patches of lighter skin and fur. It’s generally not painful or itchy.
12. Skin Tumors
- Types: Benign (like lipomas) or malignant tumors.
- Signs: Lumps or bumps on the skin, which may vary in size and appearance. Tumors should be evaluated by a vet for diagnosis and treatment options.
Tips for Managing Skin Conditions
- Regular Check-ups:
- Regular vet visits can help identify skin issues early and provide appropriate treatment.
- Proper Grooming:
- Regular brushing and bathing with appropriate products can help maintain healthy skin and coat.
- Allergy Management:
- If allergies are suspected, work with your vet to identify triggers and consider dietary adjustments or allergy medications.
- Flea and Parasite Control:
- Use preventive treatments to control fleas, ticks, and other parasites.
- Monitor Changes:
- Keep an eye on any changes in your dog’s skin or behavior and seek veterinary advice if you notice any issues.
If you notice signs of skin problems in your dog, it’s important to consult with a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.